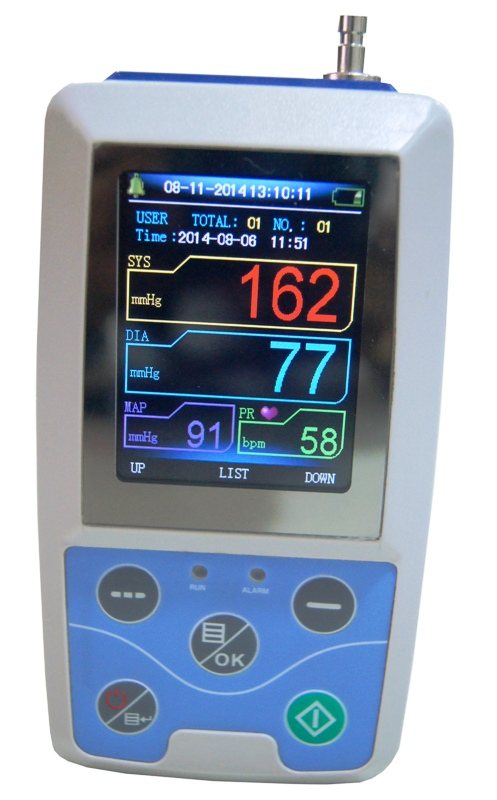
Ambulatory BP Monitor ABPM50"
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is being increasingly recommended for routine clinical practice. It may be particularly useful in evaluating the patient with variable blood pressure readings in the office, or the patient with wide discrepancies between the blood pressure readings at home and the clinician's office (ie, "white coat" hypertension). ABPM and, in particular, nocturnal blood pressure readings, may also provide prognostic data.
Ambulatory blood pressure (ABP) monitoring involves measuring blood pressure (BP) at regular intervals (usually every 15–30 minutes) over a 24 hour period while patients undergo normal daily activities, including sleep. .
What are the indications?
• Suspected white-coat hypertension (including in pregnancy)
• Suspected masked hypertension
• Suspected nocturnal hypertension or no night time reduction in BP (dipping)
• Hypertension despite appropriate treatment
• Patients with a high risk of future cardiovascular events (even if clinic BP is normal)
• Suspected episodic hypertension
• Prolonged Diabetes
Supplied with unit, Adult BP cuff, Wide BP cuff for obese patients and software.
Keywords
home
sleep
period
office
ABPM50
24 hour
Diabetes
clinician
high risk
pregnancy
BP dipping
indications
Wide BP cuff
Adult BP cuff
obese patients
time reduction
prognostic data
blood pressure BP
regular intervals
wide discrepancies
blood pressure ABP
Ambulatory BP Monitor
episodic hypertension
appropriate treatment
whitecoat hypertension
nocturnal hypertension
blood pressure readings
variable blood pressure
white coat hypertension
normal daily activities
nocturnal blood pressure
routine clinical practice
Ambulatory blood pressure
future cardiovascular events