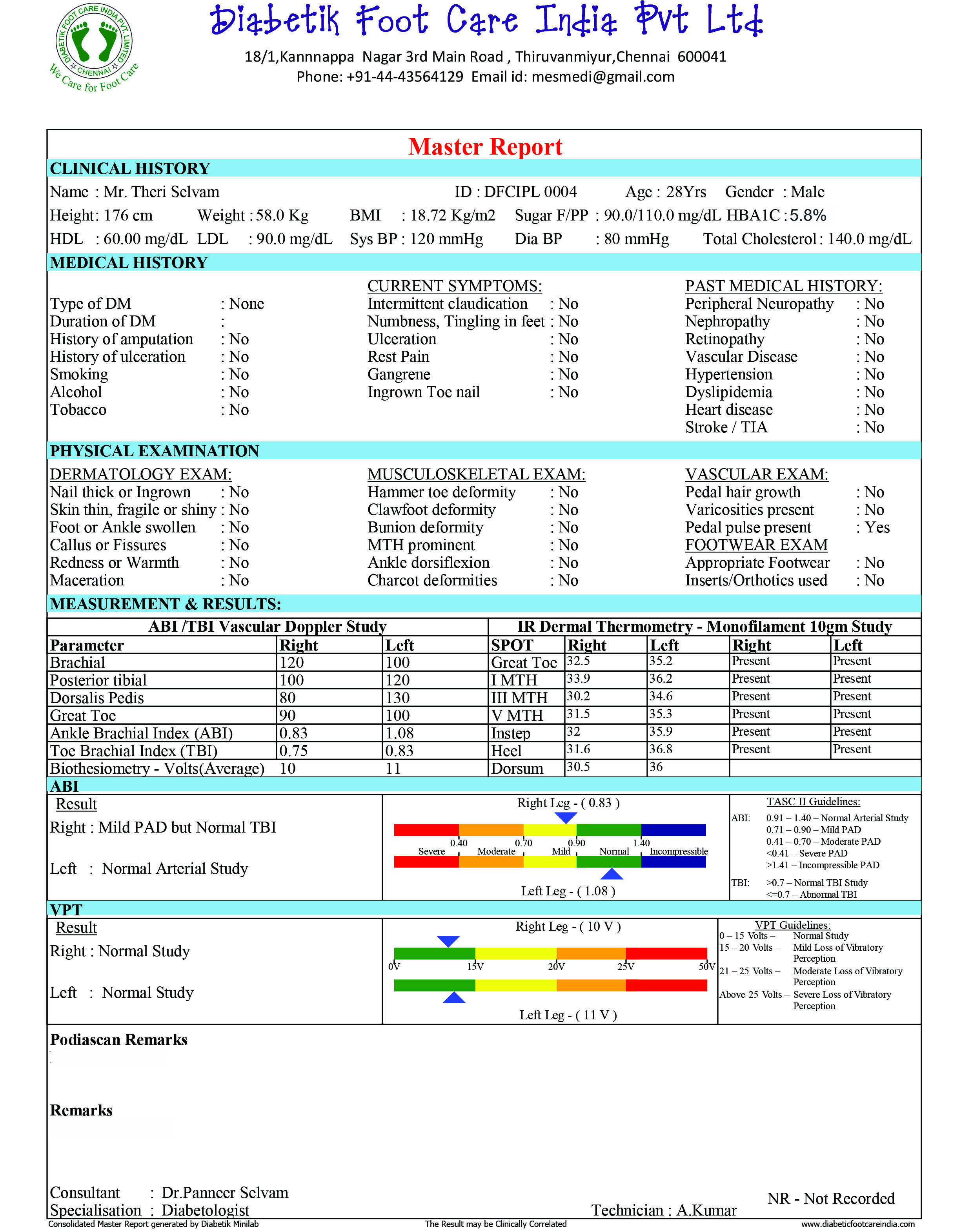
Diabetic Foot Profiler – Diabetik Minilab Vascular, Neuropathy, Foot Pressure and Foot Temperature impairments are essential measurements when testing a diabetic foot patients. Diabetik Minilab has all the above capabilities and in one device the user can test them. It is configured in a way that the technican can confidently and comfortably do a complete test on a patient in less than 15 minutes. The device is supplied with a trolley and printer. The user need to provide a Windows 7 or 8 or 10 laptop to work with this device. The Master Report generated by this device gives a complete insight about the patient parameters. Non-Invasive Testing Methods For PAD: Whenever one suspects Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), the clinician must perform a few non-invasive vascular testing methods that are commercially available and widely implemented. They include the ankle-brachial index ABI), the toe-brachial index(TBI), segmental Pressure Study and pulse volume recording(PVR) and transcutaneous oxygen monitoring(TCPO2). Ankle Brachial Index: The ankle-brachial index is the most well-known, non-invasive vascular testing tool. ABI test is performed with a Doppler and a blood pressure cuff. One calculates the ABI by dividing the ankle pressure by the brachial systolic pressure. An ABI of < 0.9 is abnormal and ABI values have a linear correlation with wound healing potential in lower extremity wounds. Patients with DM may have calcified and hardened lower extremity arterial walls that cannot be readily compressed and occluded with blood pressure cuffs. This produces falsely elevated ankle pressure readings that are often in the “normal ABI range” (0.9 to 1.4) or sometimes in the non-physiological range of above 1.4. However, Calcified leg arteries in Diabetes Mellitus or dialysis patients may yield falsely elevated ABI results. Toe-Brachial Index: The digital arteries in great toes are less affected by medial arterial calcification. One would calculate TBI by dividing the blood pressure of the great toe by the systolic brachial blood pressure. A TBI value of < 0.7 is considered abnormal. Absolute Toe pressure of > 55mmHg is considered normal. Toe pressure < 30 mmHg is considered severely ischemic. Testing Methods of Neuropathy: Diabetes can result in long-term health complications, with one of the most common being microvascular damage that leads to diabetic neuropathy (DN), which affects multiple body systems and increases amputation risk. A typical form of DN is diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), which is known to be a primary cause of balance issues, sensation loss in the feet, and a major contributor to nontraumatic lower limb amputations. Earlier detection of DPN in at-risk individuals and in those with prediabetes (PD) or type 2 diabetes (T2D) allows for potential better management through optimal intervention and lifestyle changes. Various simple neurological tests have been reported to be used for screening for DPN, some of which have also been combined into composite scoring systems to enhance the accuracy in the detection of DPN. Semmes‐Weinstein monofilament test (SWMT): The SWMT is a common screening tool for assessing the sensory function and the loss of pressure sensation (light touch perception). A 10 g monofilament test (also referred to 5.07 monofilament) is the most common in practice. Biothesiometry: Biothesiometry is a useful non-invasive tool for the detection of subclinical neuropathy in children and adolescents. The Biothesiometer is an instrument that measures the threshold of appreciation of vibration sense and the amplitude of the stimulus (measured in volts) is gradually increased until the threshold of vibratory sensation is reached, and the stimulus is appreciated by the patient. Patients with the threshold >25 volts (grade II) are at a high risk to develop ulcers later. We are a pioneer in the manufacture and export of Digital Biothesiometer and more than 10000+ are supplied to 36 countries Understanding Plantar Pressure Systems: Diabetic foot ulcer is a major source of morbidity and a leading cause of hospitalization. It is estimated that approximately 20% of hospital admissions among patients with diabetes mellitus is due to a diabetic foot ulcer. It can lead to infection, gangrene, amputation, and even death if appropriate care is not provided. Overall, the lower limb amputation in diabetic patients is 15 times higher than in non-diabetics. Understanding foot biomechanics is an important component in the evaluation of diabetic foot. The abnormal plantar pressure distribution plays a key role in the formation of plantar calluses and diabetic foot ulcer. Abnormal value of foot pressure as well as neuropathy could play an important role in the formation of plantar ulcers independently. Current international guidelines advocate achieving at least a 30 % reduction in maximum plantar pressure to reduce the risk of foot ulcers in people with diabetes. Multiple foot pressure mapping systems are available for the measurement of plantar foot pressure. In shoe and platform methods are used widely for measuring plantar foot pressure. Monitoring Temperature in the foot can prevent Ulcers: Diabetic neuropathy consists of multiple clinical manifestations of which loss of sensation is most prominent. High temperatures under the foot coupled with reduced or complete loss of sensation can predispose the patient to foot ulceration. Not only is there a high incidence of ulcerations but fighting ulcers become a relentless battle secondary to the high ulcer recurrence rate. An estimated 40 percent of foot ulcerations will recur within one year, 60 percent will recur in three years and 65 percent will recur in five years. As inflammation is a precipitating sign of ulceration, clinicians have sought techniques to identify inflammation using one of its most common symptoms, increased temperature. Randomized controlled trials have found that local areas of increased temperature, identified using simple infrared thermometers, indicate areas that are likely to ulcerate. This suggests that monitoring of foot and skin temperatures, along with subsequent offloading following observed areas of increased temperatures, can dramatically reduce the occurrence of ulcerations. One identifies areas of increased temperature using asymmetry analysis, comparing temperatures between a pair of feet. The defined threshold reported in numerous studies is an asymmetrical difference of 4ºF (2.2°C). Because most patients at risk for ulceration are also at risk for Charcot, monitoring foot temperature would be an effective tool. Should you need any further assistance please to contact us. Diabetik Foot Care India Pvt Ltd is a pioneer in the manufacturing and distribution of medical devices for the management of diabetic foot and its complications. Our Product Range: Handheld Vascular Doppler, Vascular Doppler Recorder, Automatic Vascular Doppler Recorder, Digital Biothesiometer, Podiascan, Foot Scanner, Pedography, Plantar Scan Systems, tcpO2, Monofilament 10gm, Neuropathy Therapy Stimulator, IR Light Theraphy, Podiatry chair and instruments are our major products.
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
2020-08-03T05:48:45
Diabetic Foot Profiler – Diabetik Minilab Vascular, Neuropathy, Foot Pressure and Foot Temperature impairments are essential measurements when testing a diabetic foot patients. Diabetik Minilab has all the above capabilities and in one device the user can test them. It is configured in a way that the technican can confidently and comfortably do a complete test on a patient in less than 15 minutes. The device is supplied with a trolley and printer. The user need to provide a Windows 7 or 8 or 10 laptop to work with this device. The Master Report generated by this device gives a complete insight about the patient parameters. Non-Invasive Testing Methods For PAD: Whenever one suspects Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), the clinician must perform a few non-invasive vascular testing methods that are commercially available and widely implemented. They include the ankle-brachial index ABI), the toe-brachial index(TBI), segmental Pressure Study and pulse volume recording(PVR) and transcutaneous oxygen monitoring(TCPO2). Ankle Brachial Index: The ankle-brachial index is the most well-known, non-invasive vascular testing tool. ABI test is performed with a Doppler and a blood pressure cuff. One calculates the ABI by dividing the ankle pressure by the brachial systolic pressure. An ABI of < 0.9 is abnormal and ABI values have a linear correlation with wound healing potential in lower extremity wounds. Patients with DM may have calcified and hardened lower extremity arterial walls that cannot be readily compressed and occluded with blood pressure cuffs. This produces falsely elevated ankle pressure readings that are often in the “normal ABI range” (0.9 to 1.4) or sometimes in the non-physiological range of above 1.4. However, Calcified leg arteries in Diabetes Mellitus or dialysis patients may yield falsely elevated ABI results. Toe-Brachial Index: The digital arteries in great toes are less affected by medial arterial calcification. One would calculate TBI by dividing the blood pressure of the great toe by the systolic brachial blood pressure. A TBI value of < 0.7 is considered abnormal. Absolute Toe pressure of > 55mmHg is considered normal. Toe pressure < 30 mmHg is considered severely ischemic. Testing Methods of Neuropathy: Diabetes can result in long-term health complications, with one of the most common being microvascular damage that leads to diabetic neuropathy (DN), which affects multiple body systems and increases amputation risk. A typical form of DN is diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), which is known to be a primary cause of balance issues, sensation loss in the feet, and a major contributor to nontraumatic lower limb amputations. Earlier detection of DPN in at-risk individuals and in those with prediabetes (PD) or type 2 diabetes (T2D) allows for potential better management through optimal intervention and lifestyle changes. Various simple neurological tests have been reported to be used for screening for DPN, some of which have also been combined into composite scoring systems to enhance the accuracy in the detection of DPN. Semmes‐Weinstein monofilament test (SWMT): The SWMT is a common screening tool for assessing the sensory function and the loss of pressure sensation (light touch perception). A 10 g monofilament test (also referred to 5.07 monofilament) is the most common in practice. Biothesiometry: Biothesiometry is a useful non-invasive tool for the detection of subclinical neuropathy in children and adolescents. The Biothesiometer is an instrument that measures the threshold of appreciation of vibration sense and the amplitude of the stimulus (measured in volts) is gradually increased until the threshold of vibratory sensation is reached, and the stimulus is appreciated by the patient. Patients with the threshold >25 volts (grade II) are at a high risk to develop ulcers later. We are a pioneer in the manufacture and export of Digital Biothesiometer and more than 10000+ are supplied to 36 countries Understanding Plantar Pressure Systems: Diabetic foot ulcer is a major source of morbidity and a leading cause of hospitalization. It is estimated that approximately 20% of hospital admissions among patients with diabetes mellitus is due to a diabetic foot ulcer. It can lead to infection, gangrene, amputation, and even death if appropriate care is not provided. Overall, the lower limb amputation in diabetic patients is 15 times higher than in non-diabetics. Understanding foot biomechanics is an important component in the evaluation of diabetic foot. The abnormal plantar pressure distribution plays a key role in the formation of plantar calluses and diabetic foot ulcer. Abnormal value of foot pressure as well as neuropathy could play an important role in the formation of plantar ulcers independently. Current international guidelines advocate achieving at least a 30 % reduction in maximum plantar pressure to reduce the risk of foot ulcers in people with diabetes. Multiple foot pressure mapping systems are available for the measurement of plantar foot pressure. In shoe and platform methods are used widely for measuring plantar foot pressure. Monitoring Temperature in the foot can prevent Ulcers: Diabetic neuropathy consists of multiple clinical manifestations of which loss of sensation is most prominent. High temperatures under the foot coupled with reduced or complete loss of sensation can predispose the patient to foot ulceration. Not only is there a high incidence of ulcerations but fighting ulcers become a relentless battle secondary to the high ulcer recurrence rate. An estimated 40 percent of foot ulcerations will recur within one year, 60 percent will recur in three years and 65 percent will recur in five years. As inflammation is a precipitating sign of ulceration, clinicians have sought techniques to identify inflammation using one of its most common symptoms, increased temperature. Randomized controlled trials have found that local areas of increased temperature, identified using simple infrared thermometers, indicate areas that are likely to ulcerate. This suggests that monitoring of foot and skin temperatures, along with subsequent offloading following observed areas of increased temperatures, can dramatically reduce the occurrence of ulcerations. One identifies areas of increased temperature using asymmetry analysis, comparing temperatures between a pair of feet. The defined threshold reported in numerous studies is an asymmetrical difference of 4ºF (2.2°C). Because most patients at risk for ulceration are also at risk for Charcot, monitoring foot temperature would be an effective tool. Should you need any further assistance please to contact us. Diabetik Foot Care India Pvt Ltd is a pioneer in the manufacturing and distribution of medical devices for the management of diabetic foot and its complications. Our Product Range: Handheld Vascular Doppler, Vascular Doppler Recorder, Automatic Vascular Doppler Recorder, Digital Biothesiometer, Podiascan, Foot Scanner, Pedography, Plantar Scan Systems, tcpO2, Monofilament 10gm, Neuropathy Therapy Stimulator, IR Light Theraphy, Podiatry chair and instruments are our major products.
2020-08-03T05:48:45

Submit Your Enquiry